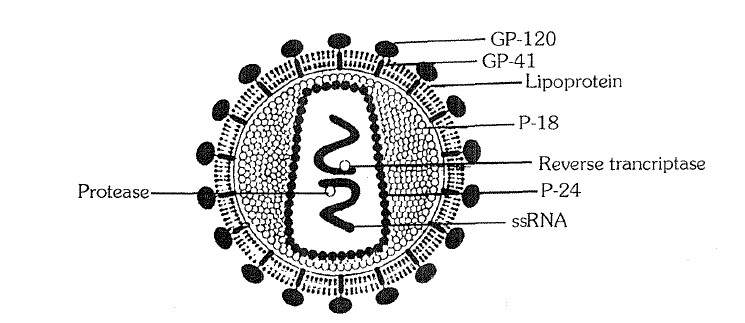
AIDS (Aquired lmmuno Deficiency Syndrome) :
The word AIDS stands for Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome.
This means deficiency of immune system, acquired during the lifetime of an individual indicating that it is not a congenital disease. 'Syndrome' means a group of symptoms. AIDS was first reported in 1981 and in the last twenty-five years or so, it has spread all over the world killing more than 25 million persons.
# Characerised by decrease in number of helper T-cells.
# Also called slim disease
# First detected in homosexual males in USA (1981) at Disease control centre Atlanta.
# In India first AIDS case was reported in 1986 from chennai.
# Virus was named variously HCLV-Ill = Human cell Leukemia Virus-III.
HTLV-III = Human T- lymphotrophic Virus-III
LAV = Lymphoadenophathy associated virus
HIV-I = Most common in India (90-120 nm) and widly distributed throughout the world.
HIV-II =Most common in West Africa (90-120 nm)
POSSIBLE ROUTES OF SPREADING :
# Sexual route : due to multiple sex partners, prostetuters, homosexuality, artificial insemination (Probability< 1%)
# Parenteral route : through blood contact due to unscreened blood transfusion, tattoeing, infected, poorly sterlised
dental instruments.
# Transplacental route -
(a) From mother to fetus, Vertical transmission, by placenta (33%)
(b) From mother to infants, perinatal transmission, by colostrum.
MISCONCEPTION :
# AIDS do not spread through more touch, physical contact, hugging, kissing, sharing meals, shaking hands, mosquito bites, coughing, sheezing looking after AIDS patients.
# HIV spreads only through body fluids.
AIDS (Aquired lmmuno Deficiency Syndrome) :
The word AIDS stands for Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome.
This means deficiency of immune system, acquired during the lifetime of an individual indicating that it is not a congenital disease. 'Syndrome' means a group of symptoms. AIDS was first reported in 1981 and in the last twenty-five years or so, it has spread all over the world killing more than 25 million persons.
# Characerised by decrease in number of helper T-cells.
# Also called slim disease
# First detected in homosexual males in USA (1981) at Disease control centre Atlanta.
# In India first AIDS case was reported in 1986 from chennai.
# Virus was named variously HCLV-Ill = Human cell Leukemia Virus-III.
HTLV-III = Human T- lymphotrophic Virus-III
LAV = Lymphoadenophathy associated virus
HIV-I = Most common in India (90-120 nm) and widly distributed throughout the world.
HIV-II =Most common in West Africa (90-120 nm)
POSSIBLE ROUTES OF SPREADING :
# Sexual route : due to multiple sex partners, prostetuters, homosexuality, artificial insemination (Probability< 1%)
# Parenteral route : through blood contact due to unscreened blood transfusion, tattoeing, infected, poorly sterlised
dental instruments.
# Transplacental route -
(a) From mother to fetus, Vertical transmission, by placenta (33%)
(b) From mother to infants, perinatal transmission, by colostrum.
MISCONCEPTION :
# AIDS do not spread through more touch, physical contact, hugging, kissing, sharing meals, shaking hands, mosquito bites, coughing, sheezing looking after AIDS patients.
# HIV spreads only through body fluids.