Characteristics of Waves :
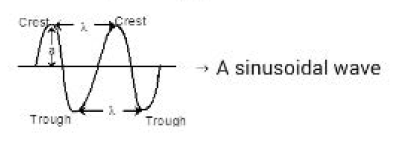
A wave is a sort of disturbance which originates from some vibrating source and travels outward as a continuous sequence of alternating crests and troughs. Every wave has five important characteristics, namely, wavelength (l), frequency (n), velocity (C), wave number `(barv)` and amplitude (`A`). See fig.
Ordinary light rays, `X`- rays, `gamma`-rays etc. are called electromagnetic radiations because similar waves can be produced by moving a charged body in a magnetic field or a magnet in an electric field. These radiations have wave characteristics and do not require any medium for their propagation.
i) `text(Wave length)` `(l)` : The distance between two neighbourinq troughs or crests is known as wavelength. It is denoted by `l` and is expressed in `cm`, `m`, nanometers (`1` nm=`10^(-9)` m). or Angstrom (`1 overset(o)(A) =10^(-10)m`); 1 micron `(mu)= 10^(-6)m, 1` milli micron `(mmu)` `=10^(-9), 1 p m = 10^(-12)` m.
ii) `text(Frequency) (nu)` : The frequency of a wave is the. number of times a wave passes through a given point in a medium in one second. It is denoted by `(nu)` and is expressed in cycles per second (cps) or hertz (Hz). 1 Hz = 1 cps.
The frequency of a wave is inversely proportional to its wave length (`l`). `n prop 1/ lambda` or `n = c/lambda`
iii) `text(Velocity)` : The distance travelled by the wave in one second is called its velocity. It is denoted by `c` and is expressed in `cm``text(sec)^(-1). `c` = `n l`` or `l = c/lambda`
iv) `text(Wave number) (barnu)` : It is defined as number of wavelengths per `cm`. It is denoted by `(bar nu)` and is expressed in `cm^(-1)`. `barnu = 1/ lambda ` (or) `barnu = v/c`
v) `text(Amplitude)` : It is the heiqht of the crest or depth of the trough of a wave and is denoted by `a`. It determines the intensity or brightness of the beam of light & is also expressed in the unit of length.
Ordinary light rays, `X`- rays, `gamma`-rays etc. are called electromagnetic radiations because similar waves can be produced by moving a charged body in a magnetic field or a magnet in an electric field. These radiations have wave characteristics and do not require any medium for their propagation.
i) `text(Wave length)` `(l)` : The distance between two neighbourinq troughs or crests is known as wavelength. It is denoted by `l` and is expressed in `cm`, `m`, nanometers (`1` nm=`10^(-9)` m). or Angstrom (`1 overset(o)(A) =10^(-10)m`); 1 micron `(mu)= 10^(-6)m, 1` milli micron `(mmu)` `=10^(-9), 1 p m = 10^(-12)` m.
ii) `text(Frequency) (nu)` : The frequency of a wave is the. number of times a wave passes through a given point in a medium in one second. It is denoted by `(nu)` and is expressed in cycles per second (cps) or hertz (Hz). 1 Hz = 1 cps.
The frequency of a wave is inversely proportional to its wave length (`l`). `n prop 1/ lambda` or `n = c/lambda`
iii) `text(Velocity)` : The distance travelled by the wave in one second is called its velocity. It is denoted by `c` and is expressed in `cm``text(sec)^(-1). `c` = `n l`` or `l = c/lambda`
iv) `text(Wave number) (barnu)` : It is defined as number of wavelengths per `cm`. It is denoted by `(bar nu)` and is expressed in `cm^(-1)`. `barnu = 1/ lambda ` (or) `barnu = v/c`
v) `text(Amplitude)` : It is the heiqht of the crest or depth of the trough of a wave and is denoted by `a`. It determines the intensity or brightness of the beam of light & is also expressed in the unit of length.
