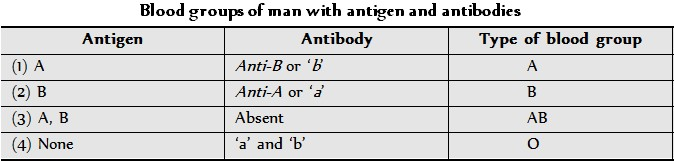
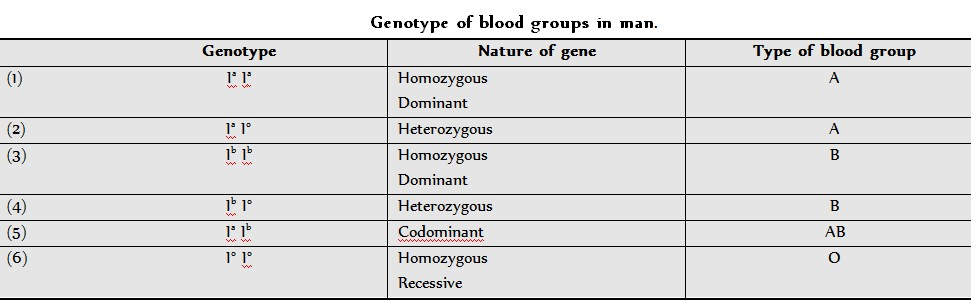
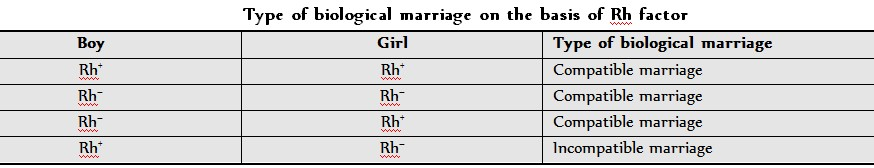
3. Multiple Alleles
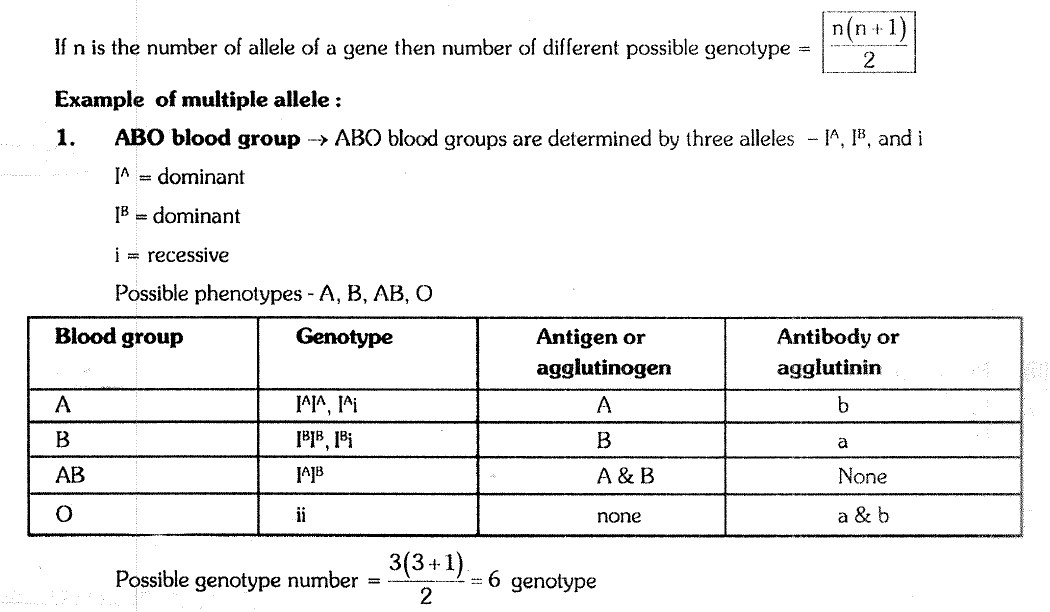
Multiple allele :- More than 2 alternative forms of same gene called as multiple allele. Multiple allele is formed due to mutation.
# Multiple alleles located on same locus of homologous chromosomes.
# A diploid individual contains two alleles and gamete contains one allele for a character.
# Multiple alleles located on same locus of homologous chromosomes.
# A diploid individual contains two alleles and gamete contains one allele for a character.