Negative Inductive Effect (`-I` Effect) :
This is due to electron-attracting groups (`X`); it develops positive charge on the chain and is said to exert a negative inductive effect denoted by (`-I`) . `overset(delta^(+))(C) -> overset(delta^(-))(X)`
`*` (`-I`) effect decreases as one goes away from group `X` (electron attracting)
`underset(3)overset(delta delta delta ^(+))(C)-underset(2)overset(delta delta ^(+))(C)-underset(1)overset(delta ^(+))(C)->X^(delta^(-))`
`C_1(delta_1+) > C_2(delta delta +) > C_3(delta delta delta +)` and after third carbon charge is negligible
`*` (` - I`) effect is in order
`text( )^(+)NH_3 NO_2 > F > COOH > Cl > Br > I > OH > C_6H_5`
Due to (`-I`) effect (electron-withdrawing nature) electron-density decreases, hence
- basic nature is decreased
- acidic nature is increased
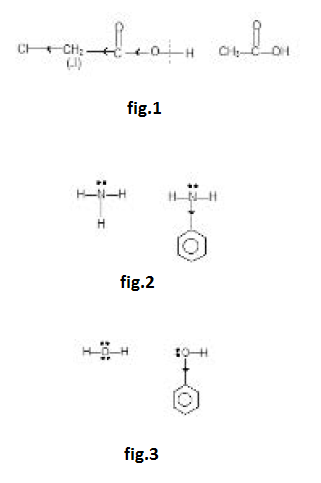
`*` Chloro acetic acid is stronger than acetic acid since `Cl` shows (`-I` effect, electron-density is decreased and `O - H` bond is weakened causing ionisation of `(-COOH)` to a greater extent than `CH_3COOH`. See fig.1.
`*` `NH_3` is a base due to lone-pair on nitrogen. Phenyl group is electron-withdrawing. What happens to electron-density of nitrogen in aniline? Naturally electron-density is decreased. Hence aniline is weaker base than `NH_3`. See fig.2.
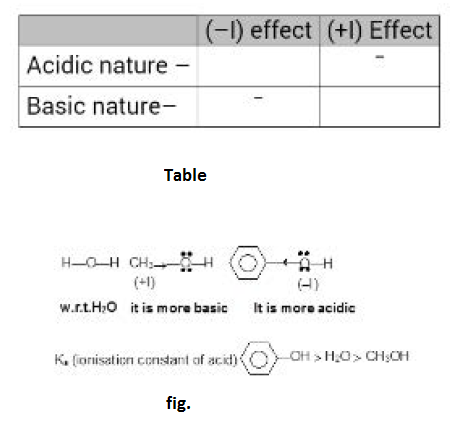
Similarly acidic nature of phenol is greater than `H_2O` due to electron-withdrawing nature of phenyl group. See fig.3.
`*` (`-I`) effect decreases as one goes away from group `X` (electron attracting)
`underset(3)overset(delta delta delta ^(+))(C)-underset(2)overset(delta delta ^(+))(C)-underset(1)overset(delta ^(+))(C)->X^(delta^(-))`
`C_1(delta_1+) > C_2(delta delta +) > C_3(delta delta delta +)` and after third carbon charge is negligible
`*` (` - I`) effect is in order
`text( )^(+)NH_3 NO_2 > F > COOH > Cl > Br > I > OH > C_6H_5`
Due to (`-I`) effect (electron-withdrawing nature) electron-density decreases, hence
- basic nature is decreased
- acidic nature is increased
`*` Chloro acetic acid is stronger than acetic acid since `Cl` shows (`-I` effect, electron-density is decreased and `O - H` bond is weakened causing ionisation of `(-COOH)` to a greater extent than `CH_3COOH`. See fig.1.
`*` `NH_3` is a base due to lone-pair on nitrogen. Phenyl group is electron-withdrawing. What happens to electron-density of nitrogen in aniline? Naturally electron-density is decreased. Hence aniline is weaker base than `NH_3`. See fig.2.
Similarly acidic nature of phenol is greater than `H_2O` due to electron-withdrawing nature of phenyl group. See fig.3.