Types of Phosphorous :
(i) Yellow or white Phosphorous (ii) Red Phosphorous (iii) Black Phosphorous
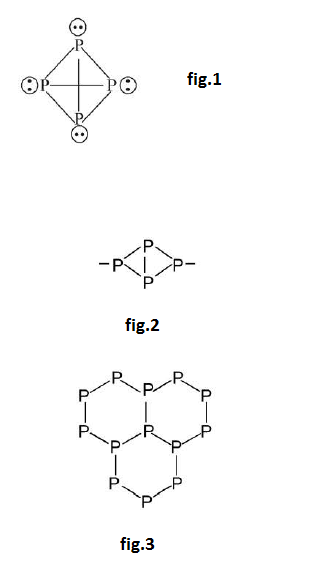
`(i)` `text(White)` `P :` See fig.1.
(a) White `P` exist as discrete `P_4` molecules. It has tetrahedral geometry. Bond angle is `60^o` instead of `109^o`. With this Bond angle white `P` is associated with strain and because it is less stable or more reactive.
(b) Ignition temp. of white `P` is `30^oC` i.e. it is highly reactive and when it undergoes ignition, it releases large amount of energy and this energy is emitted in form of light which is called as Fluorescence. i.e. white `P` glows into dark.
(c) Because of high reactivity of white `P` it is stored on `H_2O`.
(d) White `P` slowly changes into Red `P` and it will get yellow colouration and finally Red.
(e) If Red `P` has little `%` of white `P` in it as impurity then it is purified by adding `NaOH` white `P` undergoes reaction whereas red `P` not.
(f) White `P` is highly poisonous.
(ii) `text(Red)` `P :` See fig.2.
(a) Formed from white `P` by breakage of one `P-P` bond and so chain of `P_4` molecules is formed.
(b) Long chain of `P_4` molecules are formed and when compared with white `P`, red `P` has more density, less reactive with Breakage of `P-P` bond, strain related with `P_4` molecules decreases.
(c) Ignition temp. of red `P` is above `230^oC`.
(iii) `text(Black)` `P :` See fig.3.
(a) Exist in the form of Hexagonal layers like graphite.
(b) It is least reactive and has maximum density.
(c) Black `P` exist as solid of high density.
(d) It is a conductor of electricity.
`(i)` `text(White)` `P :` See fig.1.
(a) White `P` exist as discrete `P_4` molecules. It has tetrahedral geometry. Bond angle is `60^o` instead of `109^o`. With this Bond angle white `P` is associated with strain and because it is less stable or more reactive.
(b) Ignition temp. of white `P` is `30^oC` i.e. it is highly reactive and when it undergoes ignition, it releases large amount of energy and this energy is emitted in form of light which is called as Fluorescence. i.e. white `P` glows into dark.
(c) Because of high reactivity of white `P` it is stored on `H_2O`.
(d) White `P` slowly changes into Red `P` and it will get yellow colouration and finally Red.
(e) If Red `P` has little `%` of white `P` in it as impurity then it is purified by adding `NaOH` white `P` undergoes reaction whereas red `P` not.
(f) White `P` is highly poisonous.
(ii) `text(Red)` `P :` See fig.2.
(a) Formed from white `P` by breakage of one `P-P` bond and so chain of `P_4` molecules is formed.
(b) Long chain of `P_4` molecules are formed and when compared with white `P`, red `P` has more density, less reactive with Breakage of `P-P` bond, strain related with `P_4` molecules decreases.
(c) Ignition temp. of red `P` is above `230^oC`.
(iii) `text(Black)` `P :` See fig.3.
(a) Exist in the form of Hexagonal layers like graphite.
(b) It is least reactive and has maximum density.
(c) Black `P` exist as solid of high density.
(d) It is a conductor of electricity.