Cell cycle

Howard and Pelc (1953) first time described it. The sequence of events which occur during cell growth and cell division are collectively called cell cycle. Cell cycle completes in two steps:
(i) Interphase
(ii) M-phase/Dividing phase
# (i) Interphase : It is the period between the end of one cell division to the beginning of next cell division. It is also called resting phase or not dividing phase. But, it is actually highly metabolic active phase, in which cell prepares itself for next cell division. In case of human beings it will take approx 25 hours. Interphase is completed in to three successive stages.
G1 phase/Post mitotic/Pre-DNA synthetic phase/Gap Ist : In which following events take place.
(a) Intensive cellular synthesis.
(b) Synthesis of rRNA, mRNA ribosomes and proteins.
(c) Metabolic rate is high.
(d) Cells become differentiated.
(e) Synthesis of enzymes and ATP storage.
(f) Cell size increases.
(g) Decision for a division in a cell occurs.
(h) Substances of G stimulates the onset of next S – phase.
(i) Synthesis of NHC protein, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids.
(j) Longest and most variable phase.
(k) Synthesis of enzyme, amino acids, nucleotides etc. but there is no change in DNA amount.
# S-phase/Synthetic phase
(a) DNA replicates and its amount becomes double (2C - 4C).
(b) Synthesis of histone proteins.
(c) Euchromatin replicates earlier than heterochromatin.
(d) Synthesis of NHC (non-histone chromosomal proteins).
(e) Each chromosome has 2 chromatids.
# G2-phase/Pre mitotic/Post synthetic phase/gap-IInd
(a) Intensive cellular synthesis.
(b) Increase in energy store.
(c) Mitotic spindle protein (tubulin) synthesis begins.
(d) Chromosome condensation factor appears.
(e) Synthesis of 3 types of RNA and NHC proteins.
(f) Synthesis of ATP molecule and storage.
(g) Duplication of mitochondria, plastids and other cellular macromolecular complements.
(h) Damaged DNA repair occur.
# (ii) M-phase/Dividing phase/Mitotic phase
(a) Nuclear division i.e. karyokinesis occurs in 4 phases – prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. It takes 5-10% (shortest phase) time of whole division.
(b) Cytokinesis : Division of cytoplasm into 2 equal parts. In animal cell, it takes place by cell furrow method and in plant cells by cell plate method.
# Duration of cell cycle : It depends on the type of cell and external factors such as temperature, food and oxygen. Time period for , S and M-phase is species specific under specific environmental conditions. e.g. 20 minutes for bacterial cell, 8-10 hours for intestional epithelial cell, and onion root tip cells may take 20 hours.
# Regulation of cell cycle : Stage of regulation of cell cycle is phase during which a cell may follow one of the three options.
(i) It may start a new cycle, enter the S-phase and finally divide.
(ii) It may be arrested at a specific point of phase.
(iii) It may stop division and enter quiscent stage. But when conditions change, cell in phase can resume the growth and reenter the phase.
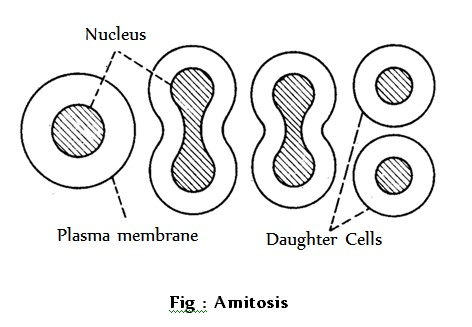
Types of cell division : It is of three types, Amitosis, Mitosis and Meiosis.
(i) Interphase
(ii) M-phase/Dividing phase
# (i) Interphase : It is the period between the end of one cell division to the beginning of next cell division. It is also called resting phase or not dividing phase. But, it is actually highly metabolic active phase, in which cell prepares itself for next cell division. In case of human beings it will take approx 25 hours. Interphase is completed in to three successive stages.
G1 phase/Post mitotic/Pre-DNA synthetic phase/Gap Ist : In which following events take place.
(a) Intensive cellular synthesis.
(b) Synthesis of rRNA, mRNA ribosomes and proteins.
(c) Metabolic rate is high.
(d) Cells become differentiated.
(e) Synthesis of enzymes and ATP storage.
(f) Cell size increases.
(g) Decision for a division in a cell occurs.
(h) Substances of G stimulates the onset of next S – phase.
(i) Synthesis of NHC protein, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids.
(j) Longest and most variable phase.
(k) Synthesis of enzyme, amino acids, nucleotides etc. but there is no change in DNA amount.
# S-phase/Synthetic phase
(a) DNA replicates and its amount becomes double (2C - 4C).
(b) Synthesis of histone proteins.
(c) Euchromatin replicates earlier than heterochromatin.
(d) Synthesis of NHC (non-histone chromosomal proteins).
(e) Each chromosome has 2 chromatids.
# G2-phase/Pre mitotic/Post synthetic phase/gap-IInd
(a) Intensive cellular synthesis.
(b) Increase in energy store.
(c) Mitotic spindle protein (tubulin) synthesis begins.
(d) Chromosome condensation factor appears.
(e) Synthesis of 3 types of RNA and NHC proteins.
(f) Synthesis of ATP molecule and storage.
(g) Duplication of mitochondria, plastids and other cellular macromolecular complements.
(h) Damaged DNA repair occur.
# (ii) M-phase/Dividing phase/Mitotic phase
(a) Nuclear division i.e. karyokinesis occurs in 4 phases – prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. It takes 5-10% (shortest phase) time of whole division.
(b) Cytokinesis : Division of cytoplasm into 2 equal parts. In animal cell, it takes place by cell furrow method and in plant cells by cell plate method.
# Duration of cell cycle : It depends on the type of cell and external factors such as temperature, food and oxygen. Time period for , S and M-phase is species specific under specific environmental conditions. e.g. 20 minutes for bacterial cell, 8-10 hours for intestional epithelial cell, and onion root tip cells may take 20 hours.
# Regulation of cell cycle : Stage of regulation of cell cycle is phase during which a cell may follow one of the three options.
(i) It may start a new cycle, enter the S-phase and finally divide.
(ii) It may be arrested at a specific point of phase.
(iii) It may stop division and enter quiscent stage. But when conditions change, cell in phase can resume the growth and reenter the phase.
Types of cell division : It is of three types, Amitosis, Mitosis and Meiosis.