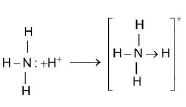
Physical Properties :
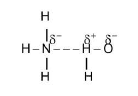
(i) Ammonia is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. It brings tears into the eyes.
(ii) It is lighter than air.
(iii) It is highly soluble in water . One volume of water dissolves `1300` volume of ammonia at `0^oC` and `1` atmosphere. The high solubility is due to the hydrogen bonding. The solubility of ammonia increase with increase of pressure and decreases with increase of temperature. See fig.
(iv) It can be easily liquefied at room temperature by the application of pressure. The liquid ammonia is colorless and boils at `-33^oC`. It freezes at `-78^oC`. Liquid ammonia has a large heat of vaporization ( `327` cal/g). It is, therefore, used in ice-plants.
(ii) It is lighter than air.
(iii) It is highly soluble in water . One volume of water dissolves `1300` volume of ammonia at `0^oC` and `1` atmosphere. The high solubility is due to the hydrogen bonding. The solubility of ammonia increase with increase of pressure and decreases with increase of temperature. See fig.
(iv) It can be easily liquefied at room temperature by the application of pressure. The liquid ammonia is colorless and boils at `-33^oC`. It freezes at `-78^oC`. Liquid ammonia has a large heat of vaporization ( `327` cal/g). It is, therefore, used in ice-plants.