ECG - Electrocardiogram
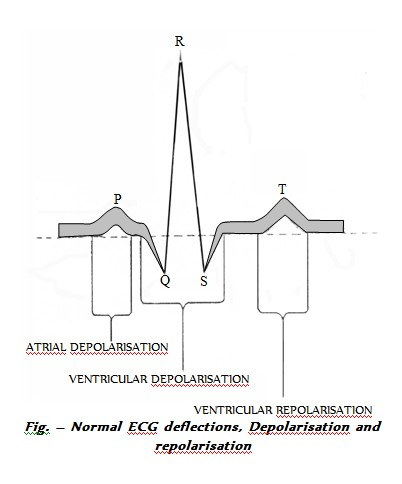
A graphic record of electrical events occuring during a cardiac cycle is called Electrocardiogram. The instrument used for rcording the heart’s electrical variations is called Electrocardiograph in which the potential differences of heart muscles are recorded by a galvanometer. In ECG, there are 2 types of waves :
# (i) Depolarisation waves : They represent the generation of the potential difference. These waves appear only when both electrodes of galvanometer are in different fields. When both the electrodes are in same field, there is no deflection and wave drops down to base line.
# (ii) Repolarisation waves : They appear when depolarisation is over and the muscle fibre is returning to its original polarity. When both electrodes are in same polarity (means 100% repolarisation and 100% depolarisation), there is no deflection.
A normal ECG has 5 deflection waves – P, Q, R, S and T. Out of them – P, R and T waves are above the base line and are called positive waves. The Q and S waves are below base line and are called negative waves. The port of the base line between any 2 deflections is called Interval.
# P wave : Indicates impulse of contraction generated by S.A. node and its spread in atria causing atrial depolarisation. The interval PQ represents atrial contraction and takes 0.1 second.
# QRS complex : Indicates spread of impulse of contraction from A.V node to the wall of ventricles through bundle of His and pukinje fibres causing ventricular depolarisation. This complex also represents repolarization of S.A. node.
The RS of QRS wave and ST interval show ventricular contraction (0.3 seconds). QRS is related to ventricular systole.
# T wave : Indicates repolarisation during ventricular relaxation.
Any abnormality in the working of heart alters the wave pattern of ECG. Thus, ECG is of great diagnostic value in cardiac diseases. ECG also indicates the rate of heart beat.
- If S.A. node is degenerated, the P wave disappears. This condition is called Heart fail. Atrial repolarisation wave is not seen in normal ECG because at this time, the depolarisation wave of ventricles is being recorded. When there is degeneration of bundle of His, the P to R interval increases. This is called Wenckebach phenomenon.
- If bundle of His is completely cut, the P-R interval becomes infinite as the bundle of His is to transmit the cardiac impulses. It is called total heart fail or total heart block. In arborisation heart block, the defect lies in purkinje fibres. In heart attack, T waves become negative. When there is decrease in blood supply to a part of heart, there occurs death of myocardium. This condition is called Myocardial infarction (MI). It is acute heart attack. The ST part of ECG is depressed when heart muscles receive insufficient oxygen and is elevated in acute MI. When there is degeneration of myocardium and deposition of fibres, the condition is called fibrillation during which, ECG obtained is bizzare or non-decipherable.
- Vector cardiogram : Represents the direction of transmission of impulse.
- History of ECG : The ECG was first recorded by Waller in frog. First human ECG was prepared by Einthoven who also discovered the electrocardiograph and discussed the principles of ECG. Hence, he is commonly called “Father of Electrocardiography”.
# (i) Depolarisation waves : They represent the generation of the potential difference. These waves appear only when both electrodes of galvanometer are in different fields. When both the electrodes are in same field, there is no deflection and wave drops down to base line.
# (ii) Repolarisation waves : They appear when depolarisation is over and the muscle fibre is returning to its original polarity. When both electrodes are in same polarity (means 100% repolarisation and 100% depolarisation), there is no deflection.
A normal ECG has 5 deflection waves – P, Q, R, S and T. Out of them – P, R and T waves are above the base line and are called positive waves. The Q and S waves are below base line and are called negative waves. The port of the base line between any 2 deflections is called Interval.
# P wave : Indicates impulse of contraction generated by S.A. node and its spread in atria causing atrial depolarisation. The interval PQ represents atrial contraction and takes 0.1 second.
# QRS complex : Indicates spread of impulse of contraction from A.V node to the wall of ventricles through bundle of His and pukinje fibres causing ventricular depolarisation. This complex also represents repolarization of S.A. node.
The RS of QRS wave and ST interval show ventricular contraction (0.3 seconds). QRS is related to ventricular systole.
# T wave : Indicates repolarisation during ventricular relaxation.
Any abnormality in the working of heart alters the wave pattern of ECG. Thus, ECG is of great diagnostic value in cardiac diseases. ECG also indicates the rate of heart beat.
- If S.A. node is degenerated, the P wave disappears. This condition is called Heart fail. Atrial repolarisation wave is not seen in normal ECG because at this time, the depolarisation wave of ventricles is being recorded. When there is degeneration of bundle of His, the P to R interval increases. This is called Wenckebach phenomenon.
- If bundle of His is completely cut, the P-R interval becomes infinite as the bundle of His is to transmit the cardiac impulses. It is called total heart fail or total heart block. In arborisation heart block, the defect lies in purkinje fibres. In heart attack, T waves become negative. When there is decrease in blood supply to a part of heart, there occurs death of myocardium. This condition is called Myocardial infarction (MI). It is acute heart attack. The ST part of ECG is depressed when heart muscles receive insufficient oxygen and is elevated in acute MI. When there is degeneration of myocardium and deposition of fibres, the condition is called fibrillation during which, ECG obtained is bizzare or non-decipherable.
- Vector cardiogram : Represents the direction of transmission of impulse.
- History of ECG : The ECG was first recorded by Waller in frog. First human ECG was prepared by Einthoven who also discovered the electrocardiograph and discussed the principles of ECG. Hence, he is commonly called “Father of Electrocardiography”.