Victor Meyer Test :
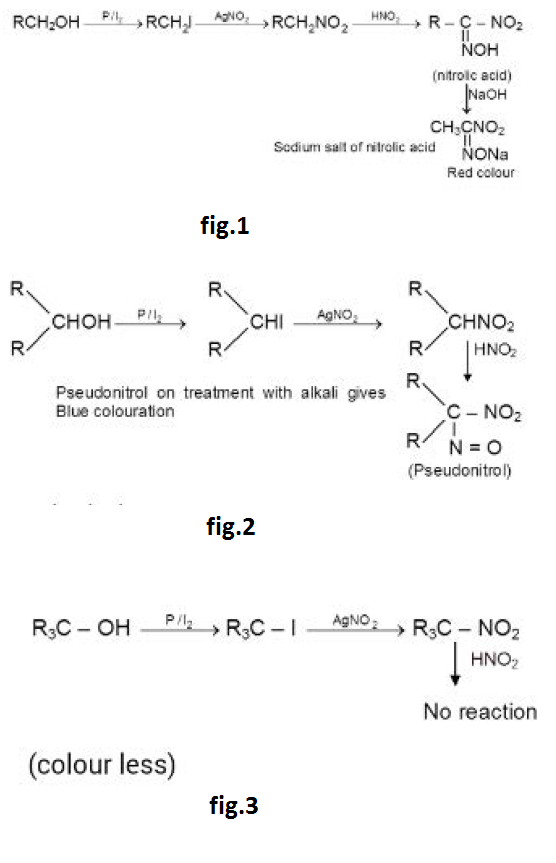
`1^o` alcohol : See fig.1.
Nitrolic acid on treatment with alkali gives colouration
`2^o` alcohol : See fig.2.
`3^o` alcohol : See fig.3.
Nitrolic acid on treatment with alkali gives colouration
`2^o` alcohol : See fig.2.
`3^o` alcohol : See fig.3.