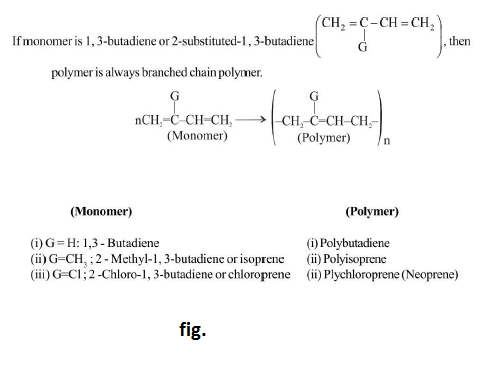
Condensation polymerisation :
(a) They are formed due to condensation reactions.
(b) Condensation polymerisation is also known as step growth polymerisation.
(c) For condensation polymerisation, monomers should have at least two functional groups. Both functional groups may be same or different.
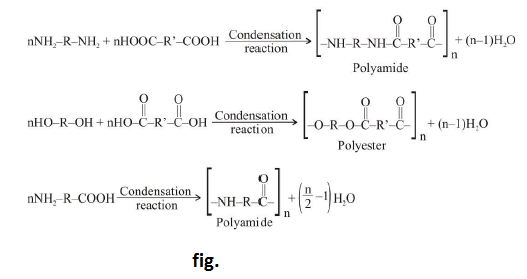
(d) Monomers having only two functional group always give linear polymer. For example : See fig.
(e) Condensation polymers do not contain all atoms initially present in the monomers. Some atoms are lost in the form of small molecules.
(f) Monomer having three functional groups always gives cross-linked polymer. Examples are : Urea-formaldehyde resin, phenol-formaldehyde resin.
(b) Condensation polymerisation is also known as step growth polymerisation.
(c) For condensation polymerisation, monomers should have at least two functional groups. Both functional groups may be same or different.
(d) Monomers having only two functional group always give linear polymer. For example : See fig.
(e) Condensation polymers do not contain all atoms initially present in the monomers. Some atoms are lost in the form of small molecules.
(f) Monomer having three functional groups always gives cross-linked polymer. Examples are : Urea-formaldehyde resin, phenol-formaldehyde resin.