Ecological Succession
Every community undergoes a series of changes until a group of organisms is established which can live and reproduce most successfully in the area. This is called biotic succession. The term succession was coined by Hult (1885). A biotic community normally undergoes continuous changes. Generally, definite and orderly sequences of communities gradually appear in an area over a period of time. A specific sequence of development of a community is related to particular set of physical and chemical conditions. This is known as sere. The last succession in a sere is called climax or a climatic climax.
# Types : Succession is of two types :
- (1) Primary succession : It includes changes which occur when living things become established on a previously uninhabited area such as a newly exposed sea floor, lake sediments or sand dunes.
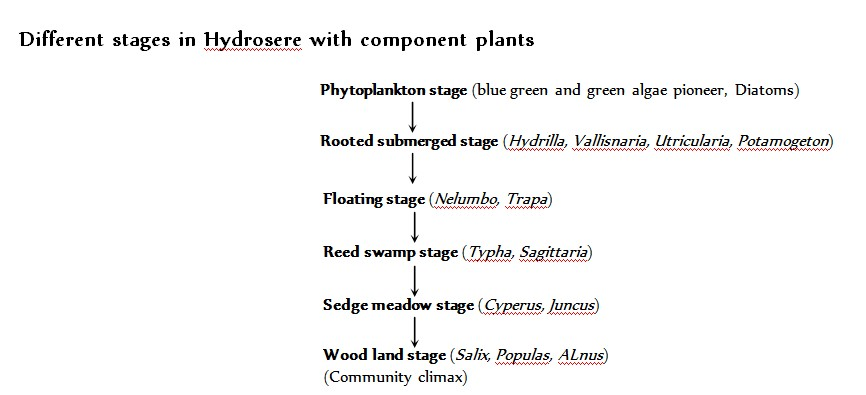
- (2) Secondary succession : It occurs where early communities have been damaged, leaving a few organisms and considerable organic matter. These remnant species, along with some new ones, regenerate a new community. Ecological succession on dry habitat, bare rock, sandy soils and aquatic habitats are called xerosere, lithosere, psammosere and hydrosere, respectively. The first plants to appear in an area are called pioneer plants. In hydrosere (or hydrach), pioneers are phytoplanktons; in lithosere, the pioneers are crustose (Saxicolous) lichens and mosses
- (3) Life forms : Raunkiaer (1934) has distinguished plants into five forms on the basis of size, shape, branching, crown, life span and perennation.
(i) Therophytes : Annual plants which perennate in the form of seeds.
(ii) Cryptophytes : Buds are occurs very deep in the soil e.g. Bulbs, rhizomes, corm, tubers etc.
(iii) Hemicryptophytes : Perennating structures occur at ground level. Aerial shoots die in the onset of winter, e.g. rosette plants.
(iv) Chemaephytes : Small plants of cold areas where perennating buds or shoot apices lie at or above the ground level.
(v) Phanerophytes : Perennial herbs, shrubs and trees, epiphytes, succulents, lianas, etc., where perennating buds occurs at 10 cm or more height above ground level.
# Types : Succession is of two types :
- (1) Primary succession : It includes changes which occur when living things become established on a previously uninhabited area such as a newly exposed sea floor, lake sediments or sand dunes.
- (2) Secondary succession : It occurs where early communities have been damaged, leaving a few organisms and considerable organic matter. These remnant species, along with some new ones, regenerate a new community. Ecological succession on dry habitat, bare rock, sandy soils and aquatic habitats are called xerosere, lithosere, psammosere and hydrosere, respectively. The first plants to appear in an area are called pioneer plants. In hydrosere (or hydrach), pioneers are phytoplanktons; in lithosere, the pioneers are crustose (Saxicolous) lichens and mosses
- (3) Life forms : Raunkiaer (1934) has distinguished plants into five forms on the basis of size, shape, branching, crown, life span and perennation.
(i) Therophytes : Annual plants which perennate in the form of seeds.
(ii) Cryptophytes : Buds are occurs very deep in the soil e.g. Bulbs, rhizomes, corm, tubers etc.
(iii) Hemicryptophytes : Perennating structures occur at ground level. Aerial shoots die in the onset of winter, e.g. rosette plants.
(iv) Chemaephytes : Small plants of cold areas where perennating buds or shoot apices lie at or above the ground level.
(v) Phanerophytes : Perennial herbs, shrubs and trees, epiphytes, succulents, lianas, etc., where perennating buds occurs at 10 cm or more height above ground level.