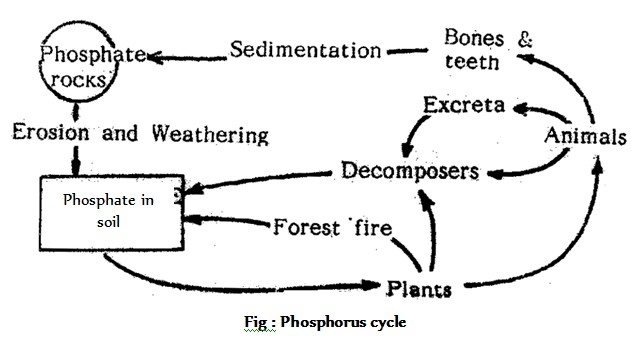
Carbon Cycle
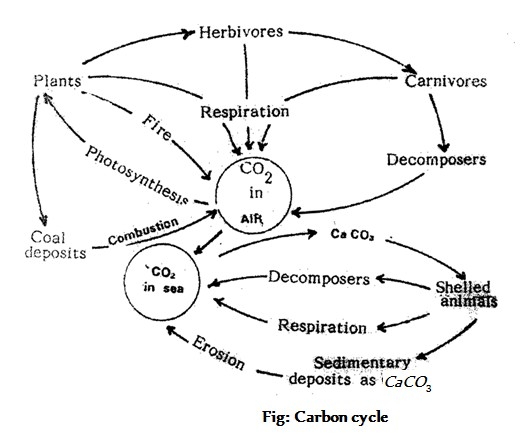
The cycling of carbon between biotic and abiotic systems is called carbon cycle. It is a gaseous cycle. The main source of carbon is the carbon dioxide (CO2). CO2 is present in the air and water. Air is the main reservoir. CO2 content of air is 0.03%. Its amount remains constant.
# (a) Flow of Carbon into the biotic system : Carbon flows into the biotic system in two ways :
Photosynthesis : Carbon enters the biotic system through photosynthesis. In photosynthesis green plants utilize CO2 and incorporate the carbon of CO2 in glucose. Glucose is used for the synthesis of other types of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. These compounds, containing carbon, are stored up in the plant tissues. When plants are eaten up by herbivores, the carbon flows into the body of herbivorous animals through food chain. When herbivores are eaten by carnivores, the carbon enters the body of carnivorus animals.
[6CO2 + 6H2O ---> C6H12O6 + 6O2.]
Formation of shell : The CO2 dissolved in sea water is utillized by the marine animals like protozoans, corals, molluscs, algae, etc., for the construction of shell. In these animals CO2 is converted into calcium carbonate (CaCO3) which is used for the construction of shells.
CO2 + H2O --> H2CO3 (Carbonic acid)
H2CO3 --> H+ + HCO3 (Bicarbonate)
HCO3 + Ca+ --> H+ + CaCO3 (Calcium carbonate)
(b) Flow of Carbon into the abiotic system : The carbon of the biotic system flows into the abiotic system in five ways :
Respiration : Plants and animals release CO2 by respiration (biological oxidation).
C6H12O6 --> CO2 + H2O + Energy
Decomposition : When plants and animals die, the dead bodies are decomposed into CO2 by decomposers like bacteria, algae, etc.
Shells : After the death of marine animals, CaCO3 stored in the shells is either deposited as sedimentary rocks or dissolved in water to release CO2 by the reversion of the above said reactions.
Coal : A certain proportion of carbon from plants is deposited as coal. Carbon from coal returns to air in the form of CO2 through combustion and weathering.
Forest fire : Combustion of wood in the forest, releases carbon from plants in the form of CO2.
# (a) Flow of Carbon into the biotic system : Carbon flows into the biotic system in two ways :
Photosynthesis : Carbon enters the biotic system through photosynthesis. In photosynthesis green plants utilize CO2 and incorporate the carbon of CO2 in glucose. Glucose is used for the synthesis of other types of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. These compounds, containing carbon, are stored up in the plant tissues. When plants are eaten up by herbivores, the carbon flows into the body of herbivorous animals through food chain. When herbivores are eaten by carnivores, the carbon enters the body of carnivorus animals.
[6CO2 + 6H2O ---> C6H12O6 + 6O2.]
Formation of shell : The CO2 dissolved in sea water is utillized by the marine animals like protozoans, corals, molluscs, algae, etc., for the construction of shell. In these animals CO2 is converted into calcium carbonate (CaCO3) which is used for the construction of shells.
CO2 + H2O --> H2CO3 (Carbonic acid)
H2CO3 --> H+ + HCO3 (Bicarbonate)
HCO3 + Ca+ --> H+ + CaCO3 (Calcium carbonate)
(b) Flow of Carbon into the abiotic system : The carbon of the biotic system flows into the abiotic system in five ways :
Respiration : Plants and animals release CO2 by respiration (biological oxidation).
C6H12O6 --> CO2 + H2O + Energy
Decomposition : When plants and animals die, the dead bodies are decomposed into CO2 by decomposers like bacteria, algae, etc.
Shells : After the death of marine animals, CaCO3 stored in the shells is either deposited as sedimentary rocks or dissolved in water to release CO2 by the reversion of the above said reactions.
Coal : A certain proportion of carbon from plants is deposited as coal. Carbon from coal returns to air in the form of CO2 through combustion and weathering.
Forest fire : Combustion of wood in the forest, releases carbon from plants in the form of CO2.