Hot Air Balloon
Hot air balloons are an ingenious application of basic scientific principles.
The basis of how the balloon works is that warmer air rises in cooler air. This is because hot air is lighter than cool air as it has less mass per unit of volume. Mass can be defined by the measure of how much matter something contains.
The actual balloon (called an envelope) has to be so large as it takes such a large amount of heated air to lift it off the ground.
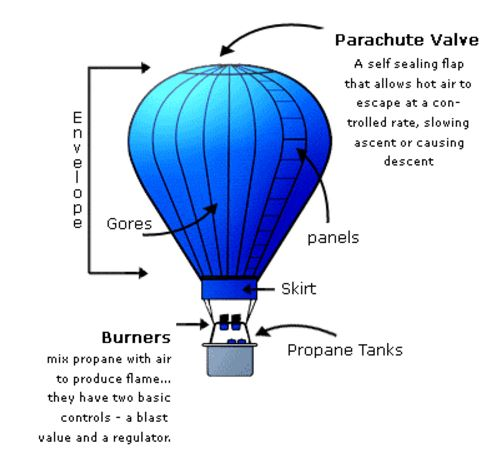
A hot air balloon is made up of 3 main parts:
`text(The Envelope)` - The actual fabric balloon which holds the air
`text(The Burner)` - The unit which propels the heat up inside the envelope
`text(The Basket)` - Where the passengers and pilot stand
The burner uses propane gas to heat up the air in the envelope to move the balloon off the ground and into the air. The pilot must keep firing the burner at regular intervals throughout the flight to ensure that the balloon continues to be stable. Naturally, the hot air will not escape from the hole at the very bottom of the envelope as firstly, hot air rises and secondly, the buoyancy keeps it moving up.
The controls for piloting a balloon are actually extremely simple.
`text(To move the balloon upwards -)` the pilot opens up the propane valve which lets the propane flow to the burner which in turn fires the flame up into the envelope. Works in much the same way as a gas grill, the more you open the valve, the bigger the flame to heat the air, the faster the balloon rises.
`text(To move the balloon downwards -)` the 'Parachute Valve' at the very top of the balloon is what is used to bring the balloon down towards the ground. It is essentially a circle of fabric cut out of the top of the envelope which is controlled by a long chord which runs down through the middle of the envelope to the basket. If the pilot wants to bring the balloon down he simply pulls on the chord which will open the valve, letting hot air escape, decreasing the inner air temperature. This cooling of air causes the balloon to slow its ascent.
The basis of how the balloon works is that warmer air rises in cooler air. This is because hot air is lighter than cool air as it has less mass per unit of volume. Mass can be defined by the measure of how much matter something contains.
The actual balloon (called an envelope) has to be so large as it takes such a large amount of heated air to lift it off the ground.
A hot air balloon is made up of 3 main parts:
`text(The Envelope)` - The actual fabric balloon which holds the air
`text(The Burner)` - The unit which propels the heat up inside the envelope
`text(The Basket)` - Where the passengers and pilot stand
The burner uses propane gas to heat up the air in the envelope to move the balloon off the ground and into the air. The pilot must keep firing the burner at regular intervals throughout the flight to ensure that the balloon continues to be stable. Naturally, the hot air will not escape from the hole at the very bottom of the envelope as firstly, hot air rises and secondly, the buoyancy keeps it moving up.
The controls for piloting a balloon are actually extremely simple.
`text(To move the balloon upwards -)` the pilot opens up the propane valve which lets the propane flow to the burner which in turn fires the flame up into the envelope. Works in much the same way as a gas grill, the more you open the valve, the bigger the flame to heat the air, the faster the balloon rises.
`text(To move the balloon downwards -)` the 'Parachute Valve' at the very top of the balloon is what is used to bring the balloon down towards the ground. It is essentially a circle of fabric cut out of the top of the envelope which is controlled by a long chord which runs down through the middle of the envelope to the basket. If the pilot wants to bring the balloon down he simply pulls on the chord which will open the valve, letting hot air escape, decreasing the inner air temperature. This cooling of air causes the balloon to slow its ascent.