DYNAMIC STATE OF BODY CONSTITUENTS
● `color{violet}"All living organisms"`, be it a simple bacterial cell, a protozoan, a plant or an animal, contain `color{violet}"thousands of organic compounds"`.
● These `color{violet}"compounds or biomolecules"` are present in `color{violet}"certain concentrations"` (expressed as `color{Brown}"mols/cell or mols/litre"` etc.).
● One of the `color{violet}"greatest discoveries"` ever made was the observation that all these biomolecules have a `color{Brown}"turn over"`.
● This means that they are `color{violet}"constantly being changed"` into some `color{violet}"other biomolecules"` and also made from some other biomolecules.
● This `color{violet}"breaking and making"` is through `color{violet}"chemical reactions"` constantly occurring in living organisms.
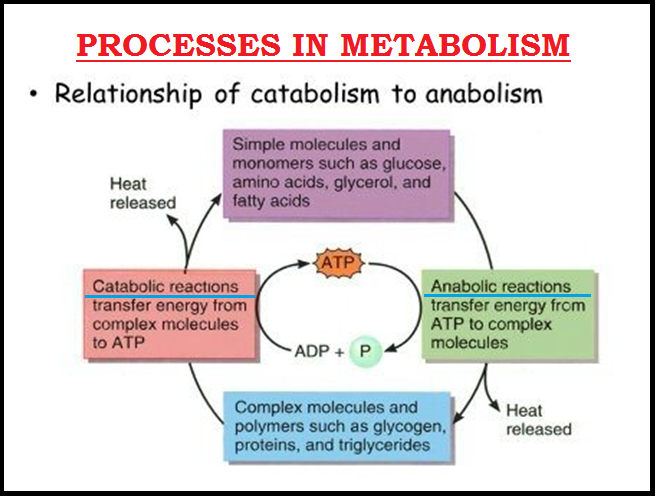
● `color{violet}"Together"` all these chemical reactions are called `color{Brown}"metabolism"`.
● Each of the `color{violet}"metabolic reactions"` results in the `color{violet}"transformation of biomolecules"`.
● A few examples for such metabolic transformations are:
`star` `color{violet}"Removal"` of `CO_2` from `color{violet}"amino acids"` making an amino acid into an amine,
`star` `color{violet}"Removal"` of amino group in a `color{violet}"nucleotide base"`
`star` `color{violet}"Hydrolysis"` of a glycosidic bond in a `color{violet}"disaccharide"`, etc.
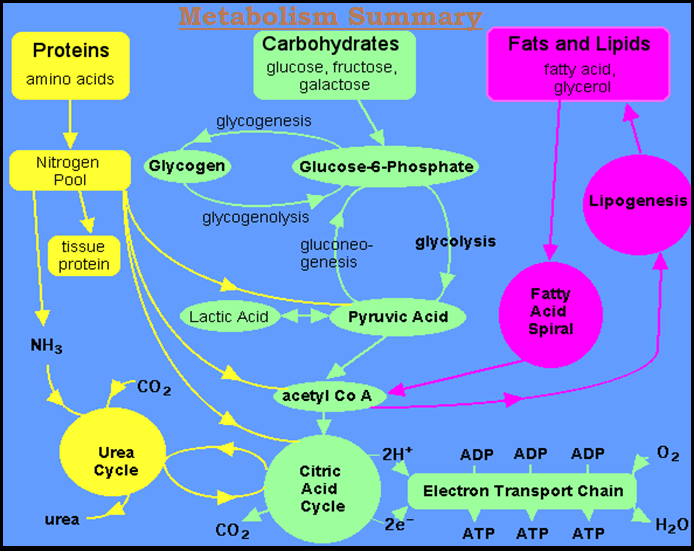
● `color{violet}"Majority"` of these metabolic reactions `color{violet}"do not occur in isolation"` but are always linked to some other reactions.
● In other words, `color{violet}"metabolites are converted"` into each other in a series of linked reactions called `color{Brown}"metabolic
pathways"`.
● These `color{violet}"metabolic pathways"` are similar to the `color{violet}"automobile traffic"` in a city.
● These pathways are either `color{violet}"linear or circular"`.
● These pathways `color{violet}"crisscross each other"`, i.e., there are `color{violet}"traffic junctions"`.
● `color{violet}"Flow of metabolites"` through metabolic pathway has a `color{violet}"definite rate and direction"` like automobile traffic.
● This `color{violet}"metabolite flow"` is called the `color{Brown}"dynamic state"` of body constituents.
● What is `color{violet}"most important"` is that this interlinked metabolic traffic is `color{violet}"very smooth"` and without a `color{violet}"single reported mishap"` for healthy conditions.
● `color{violet}"Another feature"` of these metabolic reactions is that every chemical reaction is a `color{Brown}"catalyzed reaction"`.
● There is `color{violet}"no uncatalysed metabolic"` conversion in living systems.
● Even `CO_2` dissolving in water, a `color{violet}"physical process"`, is a `color{violet}"catalysed reaction"` in living systems.
● The `color{violet}"catalysts"` which `color{violet}"hasten the rate"` of a given metabolic conversation are also `color{violet}"proteins"`.
● These proteins with `color{violet}"catalytic power"` are named `color{violet}"enzymes"`.
● These `color{violet}"compounds or biomolecules"` are present in `color{violet}"certain concentrations"` (expressed as `color{Brown}"mols/cell or mols/litre"` etc.).
● One of the `color{violet}"greatest discoveries"` ever made was the observation that all these biomolecules have a `color{Brown}"turn over"`.
● This means that they are `color{violet}"constantly being changed"` into some `color{violet}"other biomolecules"` and also made from some other biomolecules.
● This `color{violet}"breaking and making"` is through `color{violet}"chemical reactions"` constantly occurring in living organisms.
● `color{violet}"Together"` all these chemical reactions are called `color{Brown}"metabolism"`.
● Each of the `color{violet}"metabolic reactions"` results in the `color{violet}"transformation of biomolecules"`.
● A few examples for such metabolic transformations are:
`star` `color{violet}"Removal"` of `CO_2` from `color{violet}"amino acids"` making an amino acid into an amine,
`star` `color{violet}"Removal"` of amino group in a `color{violet}"nucleotide base"`
`star` `color{violet}"Hydrolysis"` of a glycosidic bond in a `color{violet}"disaccharide"`, etc.
● `color{violet}"Majority"` of these metabolic reactions `color{violet}"do not occur in isolation"` but are always linked to some other reactions.
● In other words, `color{violet}"metabolites are converted"` into each other in a series of linked reactions called `color{Brown}"metabolic
pathways"`.
● These `color{violet}"metabolic pathways"` are similar to the `color{violet}"automobile traffic"` in a city.
● These pathways are either `color{violet}"linear or circular"`.
● These pathways `color{violet}"crisscross each other"`, i.e., there are `color{violet}"traffic junctions"`.
● `color{violet}"Flow of metabolites"` through metabolic pathway has a `color{violet}"definite rate and direction"` like automobile traffic.
● This `color{violet}"metabolite flow"` is called the `color{Brown}"dynamic state"` of body constituents.
● What is `color{violet}"most important"` is that this interlinked metabolic traffic is `color{violet}"very smooth"` and without a `color{violet}"single reported mishap"` for healthy conditions.
● `color{violet}"Another feature"` of these metabolic reactions is that every chemical reaction is a `color{Brown}"catalyzed reaction"`.
● There is `color{violet}"no uncatalysed metabolic"` conversion in living systems.
● Even `CO_2` dissolving in water, a `color{violet}"physical process"`, is a `color{violet}"catalysed reaction"` in living systems.
● The `color{violet}"catalysts"` which `color{violet}"hasten the rate"` of a given metabolic conversation are also `color{violet}"proteins"`.
● These proteins with `color{violet}"catalytic power"` are named `color{violet}"enzymes"`.